前言
HITCON CTF 資安交流賽要準備兩個 CTF 題目,剛好前陣子在分析 CVE-2025-9864 的過程中學到蠻多東西
所以就把它變成能 Exploit 讓大家玩感受痛苦
剛好 Issue 頁面也還沒公開,所以大家也不能抄作業 XDDD
題目可以在這裡下載
https://github.com/qingwei4/my_CTF_challenges/tree/main/HITCON-ExhibitionCTF-2025
Patch
把 Float64ToTagged::ConversionMode 從 kCanonicalizeSmi 換成 kForceHeapNumber
當要被儲存的 value 可被 smi 表示時,kCanonicalizeSmi 會使用 smi 儲存這個 value,如果是浮點數或是超出 SMI 範圍的 integer 則會使用 HeapNumber Object
kForceHeapNumber 則一律使用 HeapNumber Object 儲存
smi 和 Heap Object 在 V8 Heap 上的差異是 smi 是直接存值,HeapNumber 儲存的是 Pointer
第二個改動則是讓 V8 不要 Crash 而已,不然沒辦法 Exploit XDDD
用到 Runtime_CheckNoWriteBarrierNeeded 的地方蠻少的,預期解是從這邊開始看
1 | diff --git a/src/maglev/maglev-reducer-inl.h b/src/maglev/maglev-reducer-inl.h |
Solution
Write Barrier
首先要了解 Write Barrier 是什麼
https://chromium.googlesource.com/v8/v8.git/+/refs/heads/12.9.16/src/heap/WRITE_BARRIER.md
它是一個用來幫助 V8 做 Garbage Collection 的機制
因為 Object 在 V8 的 Heap 上是以 Pointer 的方式儲存,而在 GC 時會移除死去的 Object,勢必會出現一些 memory fragmentation 的情境
為了要解決這種情況,V8 會搬移 Heap 上的 Object
Write Barrier 則是用來確保那些指到被搬移的 Object 的 Pointer 依然指到正確的 address 的一項機制
如果沒有 Write Barrier 紀錄的話,原本指到被搬移的 Object 的 Pointer 就不會被更新,從而變成 Dangling Pointer
Trigger UAF
MaglevReducer
舉個例子,如果一個 ValueNode 的 OpProperties 包含 kFloat64,且 Output Value 是 4.0(一個能被 smi 儲存的數值)
那它的 value_representation 就會是 ValueRepresentation::kFloat64
從第二個改動的地方開始看會發現只有 3 個 Node 在 Emit Machine Code 時用到 Runtime_CheckNoWriteBarrierNeeded
其中會發現應該要先看 StoreTaggedFieldNoWriteBarrier 這個 Node
BuildStoreTaggedFieldNoWriteBarrier() 最後也會 call 到 MaglevReducer
這個 Node 也比其他兩個 Node (StoreFixedArrayElementNoWriteBarrier / StoreMap) 常出現在 UAF 的洞之中
目前還沒看過誤用 StoreFixedArrayElementNoWriteBarrier / StoreMap 導致UAF的情況 XDDD
鎖定 StoreTaggedFieldNoWriteBarrier 後可以看這個 Node 在什麼情況下會被建出來
這邊可以慢慢找哪些地方會用到 BuildStoreTaggedFieldNoWriteBarrier()
其中 MaglevGraphBuilder::TrySpecializeStoreContextSlot() 是個蠻有趣的地方
它是在根據 runtime 蒐集到的 context(可以想成 feedback) 來優化 JavaScript 中的 store operation
當要儲存的值可以被 smi 表示時(e.g. 4.0) 就會進入 ContextCell::kSmi 的 Case 中,產出 Runtime Check 和 StoreTaggedFieldNoWriteBarrier Node
1 | MaybeReduceResult MaglevGraphBuilder::TrySpecializeStoreContextSlot( |
觀察完上述資訊後可以發現如果我能造出一個 Store Operation,它的 Input ValueNode kProperties 包含 kFloat64 且 Output Value 能被 smi 表示的話,就會獲得一個不被 Write Barrier 追蹤的 Heap Number Object
最後我選擇了 Float64Sqrt 來觸發 UAF
1 | class Float64Sqrt : public FixedInputValueNodeT<1, Float64Sqrt> { |
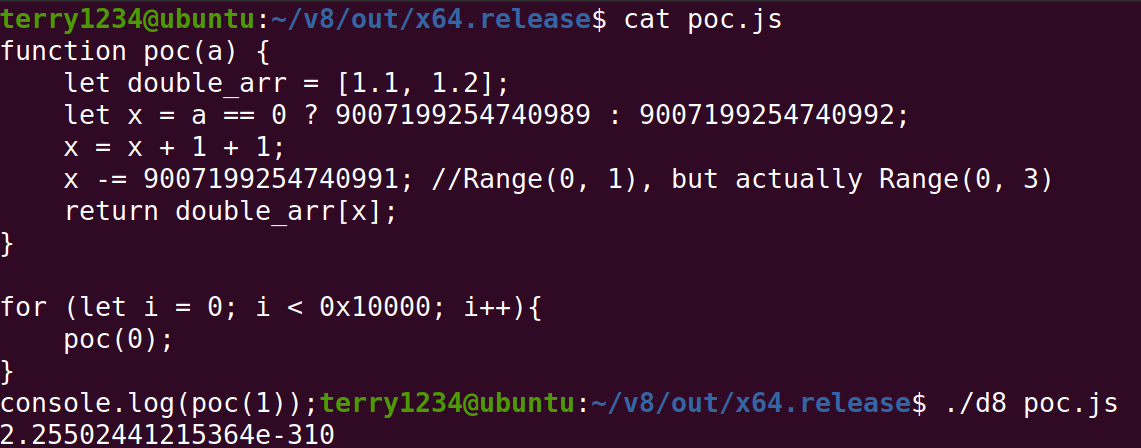
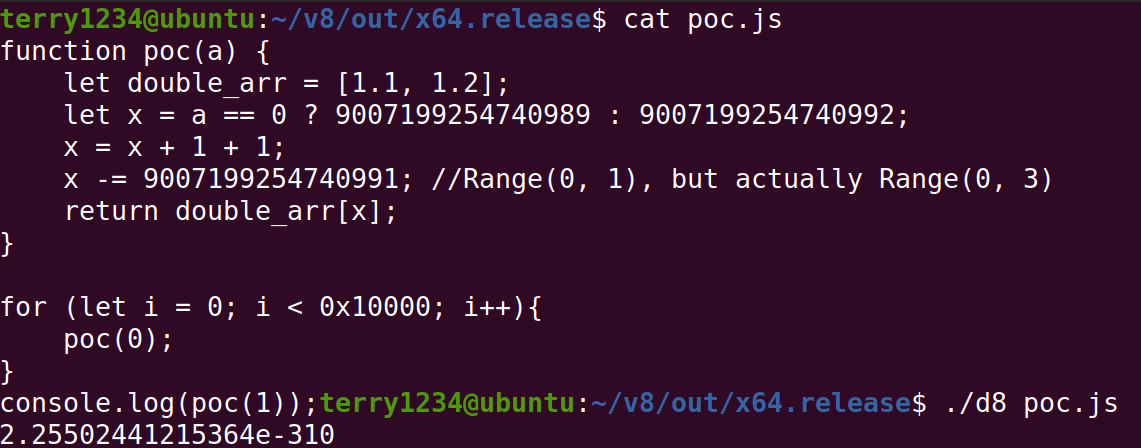
一個簡單的 poc 長這樣
1 | let v0 = 48763; |
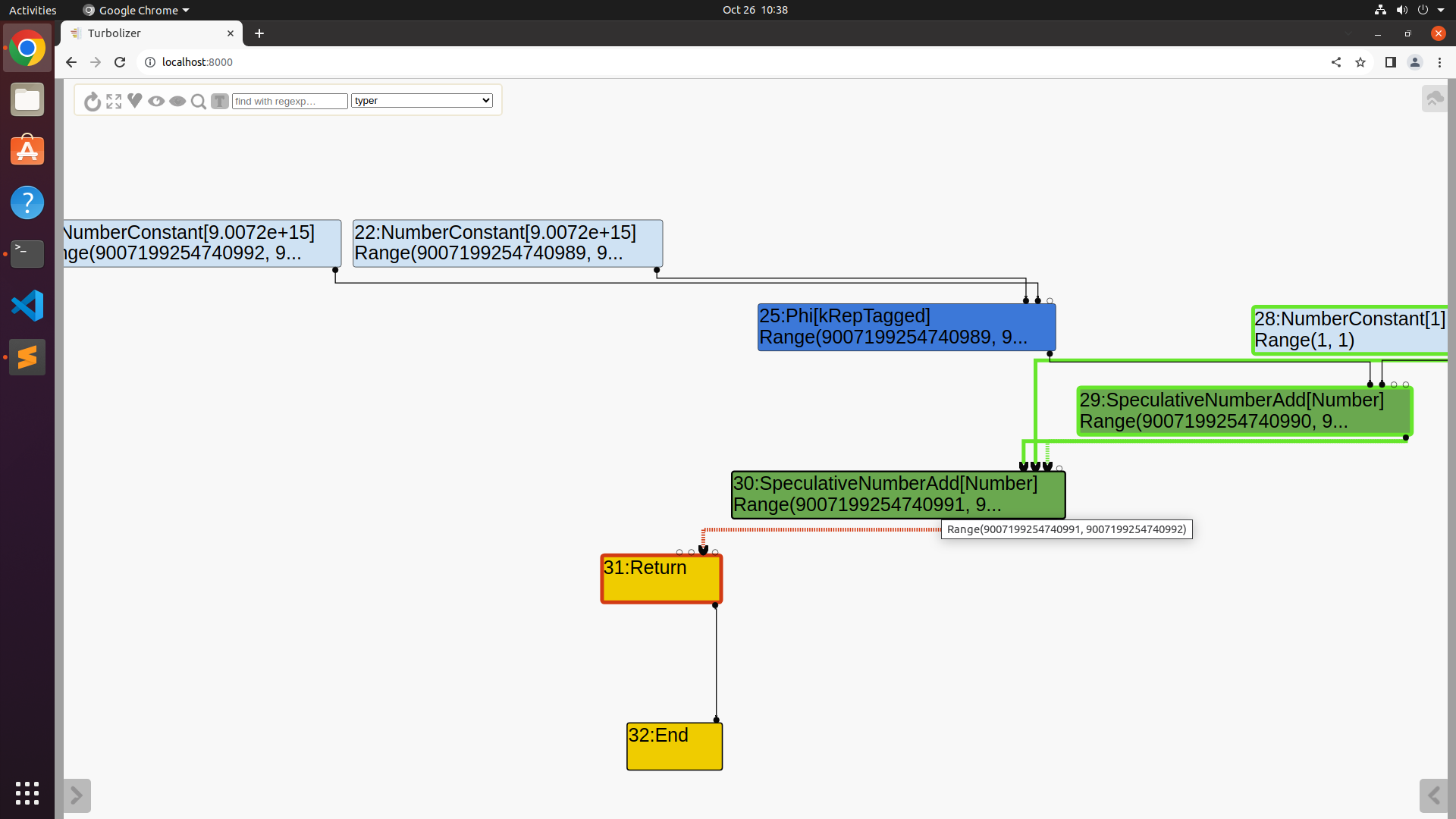
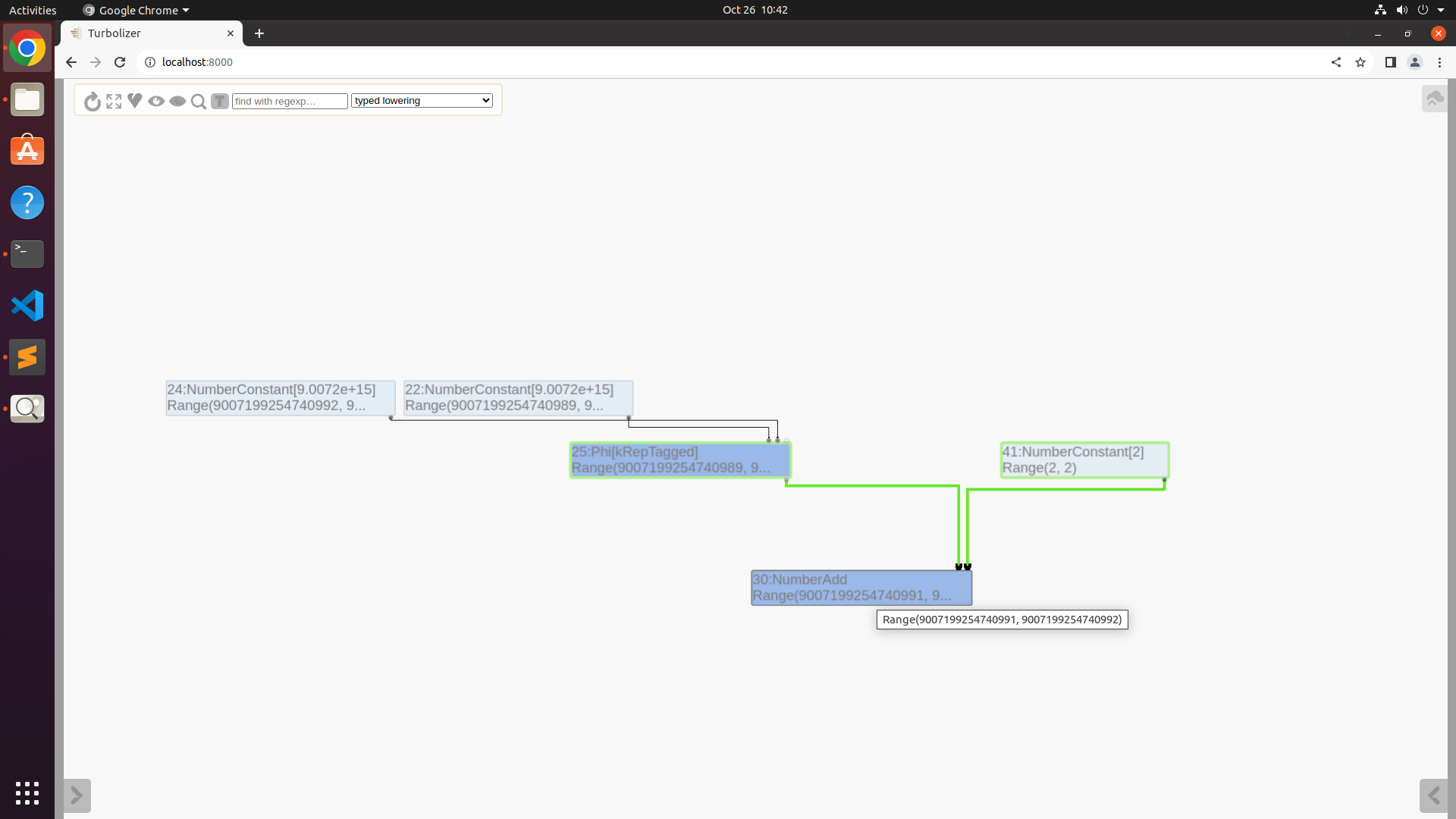
Maglev 的 IR Graph 如下
1 | 0x2ba900064a91 SharedFunctionInfo f1 (0x2ba900065625 String[6] poc.js011) |
v0 最終會指向一塊被 Free 掉的 Memory
我們可以拿回那塊 memory 並在上面偽造 Float Array
在 GC 後,Object Address 的低 32 bits 是固定的,所以可以直接用 %DebugPrint() 拿出來不用 leak
1 | scavenge_gc(); |
把偽造的 Float Array Element 指到 Object Array Element 就可以穩定 leak Object Address
指到 <address - 0x8> 就可以任意讀寫 <address> 上的資料
1 | /* |
因為沒有開 Heap Sandbox,所以可以用經典的 ArrayBuffer + WASM trick 達成 RCE
但要改的 Offset 跟傳統 Writeup 提到的不太一樣,我這邊是拿 gdb 慢慢找 offset
Exploit
For Ubuntu 22.04
一開始在寫 Exploit 的時候蠻穩定的,成功率大概有 70%,所以就開始包 Docker
等到比賽前一天主辦方給了 GCP 讓我們架題目,結果發現 Exploit 在 GCP 上的成功率變低非常多
用 %DebugPrint() 看了一下發現 Heap Number 跟 Array 的位置差的比預期多很多導致 Fake Float Array Object 失敗
我懷疑是機器的 RAM 太小導致的,所以就開始在原本寫 Exploit 的環境測
把 RAM 從 64 GB 調成 4 GB 後發現成功率確實降低很多,但當我把 RAM 從 64GB 改回 4GB 後,成功率也沒有變回來
我 Debug 了8小時還是沒找出原因,最後決定多送幾遍 Exploit看起來是我 Exploit 寫太爛導致 Heap Spray 不穩定
1 | class Helpers { |
後記
然後我在 9/20 寫好 Exploit 想說應該不用改題目了
結果有人在 10/2 早上在 X 上發了 Exploit
https://x.com/r1ngz3ro/status/1973448435614490640
後面很認真的在想要不要開 Heap Sandbox 讓大家繞的,但最後收手了 XDDD
現場沒什麼人打過 V8,所以這題沒人想解 QQ